Content Menu
● Understanding Powder Hoppers
>> Key Functions of Powder Hoppers
● Factors Influencing Hopper Size Selection
>> Production Volume and Throughput
>> Powder Characteristics
>> Space Constraints
>> Handling and Maintenance
>> Cost Considerations
● Advantages and Disadvantages of Small Powder Hoppers
>> Advantages of Small Hoppers
>> Disadvantages of Small Hoppers
● Advantages and Disadvantages of Large Powder Hoppers
>> Advantages of Large Hoppers
>> Disadvantages of Large Hoppers
● Practical Applications and Case Studies
>> Case Study 1: Small Hoppers in Pharmaceutical Production
>> Case Study 2: Large Hoppers in Cement Manufacturing
● How to Decide: Step-by-Step Hopper Size Selection
>> Step 1: Assess Your Powder Volume and Throughput Needs
>> Step 2: Evaluate Powder Characteristics
>> Step 3: Consider Facility Space and Layout
>> Step 4: Analyze Maintenance and Cleaning Protocols
>> Step 5: Calculate Budget and ROI
>> Step 6: Pilot Testing
● Installation and Safety Tips for Powder Hoppers
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
In industries where powders are processed, stored, or transported, powder hoppers play a crucial role. These containers are designed to hold and dispense powdered materials efficiently. Choosing the right size hopper—small or large—can significantly impact operational efficiency, cost, and product quality. This practical guide explores the factors influencing hopper size selection, compares small and large powder hoppers, and offers recommendations to help you make an informed choice.
Understanding Powder Hoppers
Powder hoppers are containers that temporarily hold powdered substances before further processing or packaging. They are commonly used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, construction materials, and more. A hopper's design focuses on ensuring smooth powder flow, minimizing waste, and preventing contamination.
Key Functions of Powder Hoppers
- Temporary storage of powder materials
- Controlled dispensing or feeding into other equipment
- Prevention of powder contamination and loss
- Facilitating uniform flow of powders
Factors Influencing Hopper Size Selection
Selecting the appropriate hopper size depends on several critical factors. Understanding these elements can help businesses optimize productivity and reduce operational challenges.
Production Volume and Throughput
The quantity of powder processed daily is often the most significant factor. High-volume production lines benefit from large hoppers, which minimize refill frequency and reduce downtime. Conversely, small hoppers suit low-volume or batch production where frequent changeovers are common.
Powder Characteristics
Each powder's flowability, particle size, moisture content, and abrasiveness affect hopper design. Powders prone to bridging or rat-holing may require specialized hopper shapes or flow aids, impacting size decisions. Large hoppers can pose challenges with poor-flow powders, leading to blockages.
Space Constraints
Available floor and vertical space may limit hopper size. Facilities with restricted room may prefer compact small hoppers, even if it means more frequent refilling. Conversely, spacious plants can leverage sizable hoppers to streamline operations.
Handling and Maintenance
Smaller hoppers are easier to clean, maintain, and move if needed. Large hoppers require more maintenance efforts, particularly when handling sticky or abrasive powders. Safety practices also factor into handling larger containers.
Cost Considerations
Initial investment and operational costs vary with hopper size. While large hoppers can lower labor expenses by reducing refill frequency, they typically have higher capital costs. Small hoppers, cheaper to acquire, can incur higher operational costs due to frequent handling.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Small Powder Hoppers
Advantages of Small Hoppers
- Flexibility: Ideal for small batch or specialty production runs.
- Ease of Cleaning: Smaller size simplifies cleaning and changeovers.
- Lower Initial Cost: More affordable to purchase and install.
- Better for Difficult Powders: Easier to apply flow aids and prevent clogs.
Disadvantages of Small Hoppers
- Frequent Refills: Increases downtime and labor requirements.
- Limited Storage: May not meet the demands of high-throughput operations.
- More Connections: Potentially more points for contamination or leakage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Large Powder Hoppers
Advantages of Large Hoppers
- High Capacity: Supports continuous, high-volume production without frequent interruptions.
- Reduced Labor: Lowers operational costs through fewer refills.
- Improved Flow Dynamics: When designed properly, large hoppers improve powder flow and consistency.
Disadvantages of Large Hoppers
- High Capital Cost: Requires a larger upfront investment.
- Complex Maintenance: More challenging and time-consuming to clean.
- Space Intensive: Requires significant floor and vertical space.
- Flow Challenges: Certain powders may struggle to flow through large volumes without additional equipment.
Practical Applications and Case Studies
Case Study 1: Small Hoppers in Pharmaceutical Production
A pharmaceutical company producing multiple small-batch drugs opted for small powder hoppers. The flexibility allowed fast cleaning between batches and minimized cross-contamination risk. Although labor increased due to frequent refills, the overall product quality was higher.
Case Study 2: Large Hoppers in Cement Manufacturing
A cement manufacturer handling large volumes selected massive powder hoppers designed with flow-enhancing components. The high capacity reduced downtime drastically, increasing overall plant productivity despite the higher initial cost and maintenance complexity.
How to Decide: Step-by-Step Hopper Size Selection
Step 1: Assess Your Powder Volume and Throughput Needs
Calculate the daily or hourly powder input/output and categorize your production type (batch or continuous).
Step 2: Evaluate Powder Characteristics
Consult with material experts to understand flow behavior and handling concerns.
Step 3: Consider Facility Space and Layout
Measure available space and ceiling height to determine shape and size constraints.
Step 4: Analyze Maintenance and Cleaning Protocols
Decide if ease of cleaning or maintenance frequency will impact your production schedule.
Step 5: Calculate Budget and ROI
Balance initial investment with operational efficiency and lifetime costs.
Step 6: Pilot Testing
If possible, test sample hoppers in small and large sizes under real conditions before finalizing decisions.
Installation and Safety Tips for Powder Hoppers
- Ensure secure anchoring to prevent tipping during loading or unloading.
- Incorporate dust control systems to maintain air quality.
- Use vibration or aeration devices to facilitate flow for difficult powders.
- Follow safety protocols during cleaning and maintenance to avoid exposure to hazardous materials.
- Train staff on proper handling and emergency procedures.
Conclusion
Choosing between small and large powder hoppers hinges on production volume, powder properties, space availability, maintenance capabilities, and budget constraints. Small hoppers provide flexibility and easier handling for low-volume, specialty production, while large hoppers offer efficiency and reduced labor demands for high-volume operations. Careful assessment and testing ensure optimal hopper size selection that supports operational success and product quality.
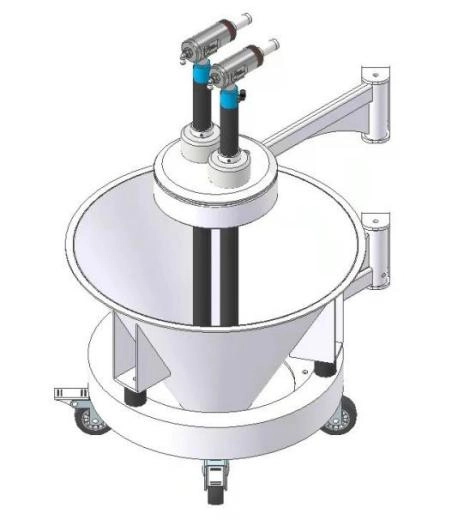

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can small hoppers handle sticky powders effectively?
Yes, small hoppers are generally better for sticky powders since they allow easier application of flow aids and quicker cleaning, reducing clogging risks.
Q2: Are large powder hoppers cost-effective for small production runs?
Typically, no. Large hoppers are more suitable for continuous or high-volume production because of the high upfront cost and maintenance.
Q3: What maintenance challenges are common with large hoppers?
Cleaning large hoppers is more labor-intensive and may require disassembly or specialized safety equipment. Flow problems like rat-holing are also more pronounced.
Q4: How does hopper size affect powder contamination risks?
More frequent refilling of small hoppers increases potential contamination points, but smaller size facilitates better cleaning. Large hoppers reduce handling but may be harder to clean thoroughly.
Q5: What are some space-saving options for large capacity requirements?
Vertical hoppers or modular hopper systems can provide large volume storage while occupying a smaller floor footprint.
Hot Tags: China, Global, OEM, private label, manufacturers, factory, suppliers, manufacturing company










































 .
. 