Content Menu
● Overview of Powder Coating
>> What is Traditional Powder Coating?
>> What are Automated Powder Coating Systems?
● Detailed Process Comparison
>> Traditional Powder Coating Process
>> Automated Powder Coating Process
● Advantages of Traditional Powder Coating
● Disadvantages of Traditional Powder Coating
● Advantages of Automated Powder Coating Systems
● Disadvantages of Automated Powder Coating Systems
● Cost Comparison
>> Initial Investment
>> Operating Costs
● Efficiency and Production Capacity
● Quality and Finish Consistency
● Environmental and Safety Considerations
>> Traditional Powder Coating Safety
>> Automated Systems Environmental Benefits
● When to Choose Traditional Powder Coating
● When to Choose Automated Powder Coating Systems
● Emerging Trends in Powder Coating Technology
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Powder coating is a popular finishing technique widely used in manufacturing to provide durable and attractive surfaces on metal and other materials. As technology advances, two primary approaches to powder coating have emerged: traditional manual powder coating and automated powder coating systems. This article provides a detailed comparison between these methods, examining their processes, advantages, drawbacks, costs, efficiency, environmental impact, and quality. The goal is to help manufacturers and decision-makers identify which powder coating method best suits their operational needs.
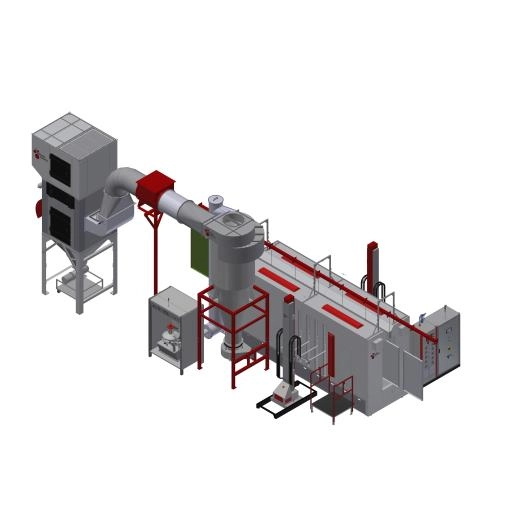
Overview of Powder Coating
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to a surface and then curing it under heat to form a solid, durable finish. The powder is usually made of fine resin particles mixed with pigments and other additives. Once applied, the powder melts and flows to create a smooth, uniform coating that is resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and abrasion.
What is Traditional Powder Coating?
Traditional powder coating typically involves manual application using spray guns operated by technicians. The process includes pre-treatment, powder spraying, curing in ovens, and final inspection. This method has been widely used for decades and remains popular in many industries.
What are Automated Powder Coating Systems?
Automated powder coating systems use robotics, conveyor belts, and computerized controls to apply powder coatings with minimal human intervention. These systems are designed for high-volume production, aiming to increase consistency, reduce labor costs, and improve throughput.
Detailed Process Comparison
Traditional Powder Coating Process
Traditional powder coating begins with surface preparation, such as cleaning, degreasing, and sometimes abrasive blasting. Operators then use manual spray guns to apply an electrostatically charged powder to the workpieces. The charged powder particles adhere to the grounded surface due to electrostatic attraction.
After application, coated parts are moved to curing ovens, where heat causes the powder to melt and form a continuous film. Once cooled, the finished product undergoes quality control inspection.
Automated Powder Coating Process
Automated systems incorporate the same fundamental steps: surface preparation, powder application, curing, and inspection. However, the powder spray is performed by robotic arms or automated guns programmed to follow highly precise movements. Conveyor systems transport parts through customized pre-treatment chambers, application booths, and curing ovens without manual handling.
Advanced sensors and software constantly monitor factors such as powder thickness, spray flow, and curing temperature, adapting the process parameters in real time to maintain consistent quality.
Advantages of Traditional Powder Coating
- Flexibility: Manual application allows operators to adjust spray angles and coverage for complex or irregular parts.
- Lower Initial Investment: Traditional setups require less capital expenditure compared to automated systems.
- Skill-Dependent: An experienced technician can produce very high-quality finishes, especially on one-off or custom jobs.
- Simple Maintenance: Manual equipment and smaller setups are easier and cheaper to maintain.
Disadvantages of Traditional Powder Coating
- Limited Throughput: Manual coating is slower and less ideal for high-volume production.
- Inconsistent Quality: Variability in operator technique can lead to uneven coatings or defects.
- Labor-Intensive: Requires skilled workers to operate spray guns continuously, increasing labor costs.
- Operator Fatigue and Safety Risks: Continuous exposure to powders and repetitive motions may pose health risks and reduce productivity.
Advantages of Automated Powder Coating Systems
- High Productivity: Automated lines can coat thousands of parts per hour, ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
- Consistent Quality: Robots apply powder uniformly, minimizing defects and rework.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Less manual intervention means fewer workers and lower labor expenses.
- Improved Safety: Automation limits human exposure to powders and chemicals.
- Data-Driven Process Control: Real-time adjustments optimize coating thickness and reduce powder waste.
Disadvantages of Automated Powder Coating Systems
- High Initial Cost: Robotic systems, conveyors, and sensors require substantial upfront investment.
- Complex Setup and Programming: Installing and calibrating automated systems demands specialized expertise.
- Less Flexibility for Custom Jobs: Handling complex shapes or small batches may be challenging.
- Maintenance Complexity: Automated equipment needs ongoing technical support and preventive maintenance to avoid downtime.
Cost Comparison
Initial Investment
Traditional powder coating typically has lower startup costs. A manual spray booth, curing oven, and basic prep equipment are relatively affordable for small and medium-sized businesses.
Automated systems require expenses for robotics, automated conveyors, advanced sensors, and software — pushing the initial investment significantly higher.
Operating Costs
Traditional methods incur higher labor expenses due to skilled operator demands. Energy costs are comparable for ovens but may be slightly lower in manual setups with smaller batch sizes.
Automated systems reduce labor costs but may have higher energy consumption because of continuous conveyor operation and advanced monitoring equipment. Maintenance and repairs of robotic systems also add to ongoing expenses.
Efficiency and Production Capacity
Manual powder coating suits low to medium production volumes or custom jobs. Typical output depends on operator skill but usually cannot match automated throughput.
Automated lines excel in high-volume manufacturing, working continuously with minimal downtime. Integration with production planning and supply chain systems further optimizes efficiency.
Quality and Finish Consistency
Human operators can deliver detailed workmanship but may introduce inconsistency. Manual coating thickness and uniformity vary between operators and shifts.
Automated systems provide tightly controlled coating parameters, resulting in highly consistent finishes. They can maintain specified thicknesses within tight tolerances and reduce rejects and touch-ups.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Traditional Powder Coating Safety
Operators are exposed to powder aerosols and solvents during cleaning and prep stages. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) and ventilation are essential. Manual spraying can also create waste through overspray.
Automated Systems Environmental Benefits
Automation can reduce powder waste by improving overspray collection efficiency. Closed-loop monitoring minimizes excess powder usage. Fewer human exposures lead to a safer working environment.
Both methods benefit from powder coating's inherent eco-friendliness — no volatile organic compounds (VOC) emissions compared to liquid paints.
When to Choose Traditional Powder Coating
- Small production runs or custom, highly detailed projects.
- Businesses with limited budget for capital investment.
- Operations needing flexible coating for diverse part geometries.
- Facilities with skilled operators already trained in manual spray techniques.
When to Choose Automated Powder Coating Systems
- Large-scale manufacturing demanding high throughput.
- Businesses focused on consistent quality and lower defect rates.
- Companies seeking to reduce long-term labor costs.
- Operations aiming for advanced process control and data integration.
- Facilities prioritizing improved workplace safety and environmental compliance.
Emerging Trends in Powder Coating Technology
- Hybrid Systems: Combining robotic automation with manual touch-up to balance flexibility and efficiency.
- IoT Integration: Using sensors and cloud-based monitoring for predictive maintenance and quality analytics.
- Advanced Materials: Development of new powders that cure faster and offer enhanced properties.
- Sustainability Focus: Further reducing waste and energy consumption through innovative coatings and equipment design.
Conclusion
Both traditional powder coating and automated powder coating systems have distinct advantages and disadvantages. Traditional methods offer flexibility and lower capital costs, making them well-suited to small or specialized operations. Automated systems provide unmatched efficiency, consistency, and reduced labor requirements, ideal for mass production environments. The right choice depends on your production volume, budget, product complexity, and desired quality standards.
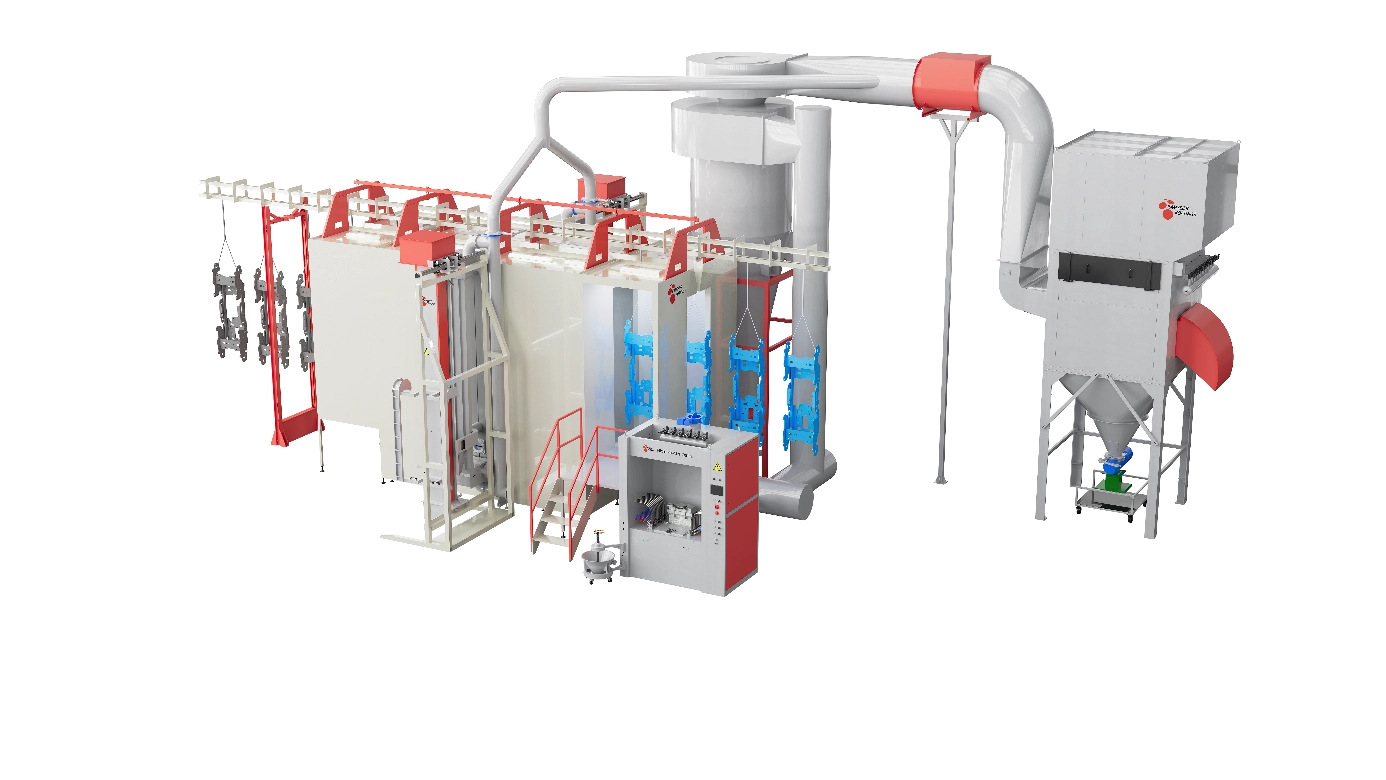
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What materials can be powder coated using traditional and automated methods?
Both methods can coat metals like steel and aluminum, as well as some plastics designed for powder coating. Material compatibility depends primarily on temperature resistance and surface preparation.
2. How does powder coating compare to liquid paint?
Powder coating results in a thicker, more durable finish with no VOC emissions and less environmental impact than liquid paint. It also generally provides better chemical and abrasion resistance.
3. Can automated powder coating systems handle complex part shapes?
While automated robots are programmed for precise movements, highly complex or irregular shapes may require manual touch-up or hybrid systems combining automation with manual application.
4. What maintenance is required for automated powder coating equipment?
Regular preventive maintenance includes cleaning spray guns and nozzles, checking conveyor systems, calibrating sensors, and software updates to ensure process stability and avoid downtime.
5. Are there size limitations for parts coated with automated powder coating systems?
Automated systems can be designed for various part sizes, but extreme sizes may require specialized machinery or manual coating. Conveyor dimensions and robot reach typically define size limits.
Hot Tags: China, Global, OEM, private label, manufacturers, factory, suppliers, manufacturing company










































 .
. 