Content Menu
● Understanding Powder Coating and Automation
● Why Automation Matters in Powder Coating
● Levels of Automation in Powder Coating
>> Level 1: Hardwired Control (Minimal Automation)
>> Level 2: Mimic Pane Automation
>> Level 3: Touch Screen Hardware Terminal Automation
>> Level 4: PC-Based Automation
>> Level 5: Fully Integrated Robotic Systems
● How to Assess Your Powder Coating Automation Needs
>> Step 1: Analyze Your Production Volume and Throughput Requirements
>> Step 2: Evaluate Product Complexity and Size
>> Step 3: Define Quality Requirements
>> Step 4: Consider Labor Availability and Costs
>> Step 5: Analyze Budget and ROI Expectations
>> Step 6: Consider Space and Infrastructure
● Designing the Powder Coating Automation System
● Matching Automation Level with Business Size and Production Scale
● Common Automation Components and Technologies in Powder Coating
● Key Factors Influencing Automation Choice
● Benefits of Choosing the Right Level of Automation
● Challenges in Implementing Automation
● Final Recommendations
● Related Questions and Answers
Choosing the right level of automation for your powder coating process involves a detailed analysis of your production needs, quality requirements, budget, and operational goals. The appropriate automation level improves efficiency, consistency, and cost-effectiveness while fitting your factory's scale and product specifications.

Understanding Powder Coating and Automation
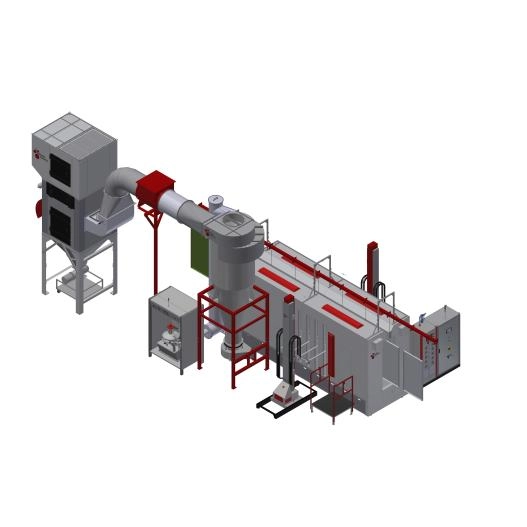
Powder coating is a finishing process where powdered paint is electrostatically applied and then cured, creating a durable and consistent surface. Automation in powder coating refers to using machinery and control systems, from basic conveyor systems to fully robotic lines, to reduce manual labor, improve precision, and increase throughput.
Why Automation Matters in Powder Coating
Automation enhances:
- Quality Consistency: Automated systems reduce human error, ensuring each part receives uniform coating thickness and coverage.
- Productivity: Automated lines can operate faster and longer than manual processes with less downtime.
- Cost Efficiency: Despite initial investments, automated systems lower labor costs, reduce waste, and optimize powder usage.
- Safety: Automation minimizes worker exposure to spray powders and hazardous environments.
- Environmental Compliance: Automated systems help meet stricter regulations by reducing emissions and overspray.
Levels of Automation in Powder Coating
Automation for powder coating finishing systems can be broken down generally into five levels, ranging from minimal automation to fully integrated robotic systems.
Level 1: Hardwired Control (Minimal Automation)
This is the most basic typical system where controls are fixed and simple. It requires significant manual intervention, and operational flexibility is minimal. Though durable, these systems are less efficient and offer less consistent quality.
Level 2: Mimic Pane Automation
At this stage, a control panel mimics system operations, allowing some automation and easier troubleshooting. Operator involvement remains high, but this level adds modest process controls.
Level 3: Touch Screen Hardware Terminal Automation
Using programmable logic controllers (PLC), this level increases automation and reduces operator intervention. Operators can control and troubleshoot via touch screens, making it easier to maintain and adjust processes.
Level 4: PC-Based Automation
Here, the system includes data collection and process monitoring, improving efficiency and flexibility. This automation facilitates part tracking, quality reporting, and predictive maintenance, requiring less manual input.
Level 5: Fully Integrated Robotic Systems
The highest automation tier includes robotic arms for spraying, loading, unloading, and even curing processes. These highly complex systems maximize throughput, minimize labor, and provide the best quality control but require skilled programmers and significant capital investment.
How to Assess Your Powder Coating Automation Needs
Step 1: Analyze Your Production Volume and Throughput Requirements
- High-volume production lines benefit from higher automation levels to maintain speed and consistency.
- Low-volume or customized production might only require partial automation or semi-automated systems.
Step 2: Evaluate Product Complexity and Size
- Complex parts with many surfaces or unusual shapes may require robotic systems for thorough and consistent coating.
- Simple geometries might be effectively coated using conveyorized systems with manual spray guns.
Step 3: Define Quality Requirements
- High-end products that require flawless finish quality justify investment in advanced automation that controls powder thickness and spray parameters precisely.
- More economical applications can tolerate manual or lower automation systems.
Step 4: Consider Labor Availability and Costs
- Regions where labor is expensive or scarce might require more automation.
- Where labor is affordable and available, lower automation might suffice for cost efficiency.
Step 5: Analyze Budget and ROI Expectations
- Fully robotic and integrated systems involve high upfront costs but reduce long-term operational expenses.
- Entry-level automation systems are less costly initially but might incur higher labor and maintenance costs.
Step 6: Consider Space and Infrastructure
- Automated systems require space, power, and sometimes specialized facilities for powder recovery and waste management.
- Evaluating existing factory infrastructure compatibility is critical for seamless integration.
Designing the Powder Coating Automation System
When planning an automated powder coating line, integrating multiple stages efficiently is essential:
- Pre-coating Preparation: Cleaning and drying steps must be automated or synchronized to prevent bottlenecks.
- Spraying Process: The core coating process, which may use robotic arms or automated spray guns.
- Curing Process: Infrared or convection ovens must be matched with the throughput capacity.
- Quality Inspection and Packaging: These phases can also be automated, including inline inspection systems.
A well-designed layout minimizes material handling and processing delays, ensuring smooth flow and optimal cycle times.
Matching Automation Level with Business Size and Production Scale
- Small Businesses or Startups: Often select entry-level or semi-automated systems providing better quality than manual coating but remaining budget-friendly.
- Medium-sized Enterprises: Benefit from mid-level automation that balances cost and productivity, including PLC-based control and controlled powder delivery.
- Large-scale Manufacturers: Invest in fully integrated robotic systems to maximize production speed, minimize wastage, and ensure consistent quality.
Common Automation Components and Technologies in Powder Coating
- Conveyor Systems: For part transport through different process zones.
- Spray Booths: Automated spray guns or robots for powder application.
- Powder Recovery Systems: To collect and recycle overspray powder efficiently.
- Control Systems: PLCs or PC-based software to manage operations and data.
- Robotic Arms: For precise coating on complex parts and loading/unloading tasks.
- Curing Ovens: For controlled baking of powder onto parts.
Key Factors Influencing Automation Choice
| Factor | Influence on Automation Level |
| Production Volume | Higher volumes justify higher automation |
| Product Complexity | Complex shapes favor robotic automation |
| Quality Standards | Higher standards demand precise control and monitoring |
| Labor Costs & Availability | Expensive labor incentivizes more automation |
| Budget Constraints | Initial investment capacity limits automation complexity |
| Factory Layout & Infrastructure | Determines feasible system integration and size |
Benefits of Choosing the Right Level of Automation
- Optimizes capital and operational expenditures
- Enhances process reliability and product quality
- Increases production capacity and flexibility
- Reduces waste and environmental impact
- Improves worker safety and ergonomics
Challenges in Implementing Automation
- High initial investment costs for advanced systems
- Need for skilled technicians and programmers
- Potential downtime during integration and training
- Infrastructure upgrades may be required
Final Recommendations
- Conduct a thorough analysis of production needs, product types, and budget.
- Start with clear automation goals—whether efficiency, cost reduction, quality, or flexibility.
- Consider scalability to accommodate future growth.
- Engage with system integrators or experts to select and customize the right system.
- Factor in training and maintenance support in the decision-making.
Related Questions and Answers
Q1: What is the difference between manual and automated powder coating systems?
A1: Manual systems rely on operators to apply powder by hand, leading to variability and slower throughput. Automated systems use machinery and controls for consistent application, higher speeds, and reduced labor dependency.
Q2: How does product complexity influence the choice of automation?
A2: Complex-shaped or large products often require robotic or advanced automated systems to ensure even coating on all surfaces, while simpler products might be coated using simpler conveyorized systems.
Q3: Can small businesses benefit from automation in powder coating?
A3: Yes, small businesses can use entry-level or semi-automated systems to improve coating quality and efficiency within budget constraints.
Q4: What are common components of a fully automated powder coating system?
A4: They include automated conveyors, robotic spray guns, powder recovery units, programmable control systems, curing ovens, and integrated inspection stations.
Q5: How does automation reduce environmental impact in powder coating?
A5: Automation optimizes powder usage, reduces overspray waste through recovery systems, and ensures compliance with emission standards by controlling process parameters efficiently.
[1] https://www.hinahcoatingline.com/news/implementing-automated-powder-coating-system-in-5-steps
[2] https://huggingface.co/facebook/xm_transformer_unity_en-hk/raw/main/en_zh_spm.dict
[3] https://productionsystems-usa.com/levels-of-automation-in-finishing-systems/
[4] https://ia800600.us.archive.org/5/items/ittushu-2470/%E6%B8%85%E5%8D%8E%E5%A4%A7%E5%AD%A6%E5%9B%BE%E4%B9%A6%E9%A6%86-%E6%88%98%E7%96%AB%E7%89%88/H_%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80%E3%80%81%E6%96%87%E5%AD%97/12133_%E5%9B%BD%E9%99%85%E4%BA%A4%E6%B5%81%E8%8B%B1%E8%AF%AD%E9%98%85%E8%AF%BB%E8%BF%9B%E9%98%B6%E6%95%99%E7%A8%8B_text.pdf
[5] https://www.wagner-group.com/us/industry/products/powder-coating/complete-systems/
[6] https://www.scribd.com/document/10317685/%E5%A4%A7%E5%AD%A6%E7%A7%91%E6%8A%80%E8%8B%B1%E8%AF%AD
[7] https://www.hinahcoatingline.com/news/information-need-to-know-about-automated-powder-coating-line-price
[8] https://www.scribd.com/document/498929761/%E5%8F%8C%E8%89%B2%E8%A1%A8%E8%A7%A3%E8%8B%B1%E8%AF%AD%E8%AF%8D%E6%B1%87
[9] https://reasonablechoice.net/en/blog/automation-of-powder-coating-application
[10] https://huggingface.co/openbmb/VisCPM-Chat/raw/main/vocab.txt
Hot Tags: China, Global, OEM, private label, manufacturers, factory, suppliers, manufacturing company










































 .
. 