Content Menu
● Understanding the role of powder hoppers
● Key design features to look for
● Capacity and discharge rate considerations
● Material compatibility and coatings
● Cleaning, sanitation, and regulatory considerations
● Installation and integration tips
● Popular materials and brands
● Maintenance best practices
● Customization options worth considering
● Environmental and safety considerations
● Selecting the right hopper for your application
● Case study: optimizing a coating line
● Practical tips for evaluating vendors
● Maintenance checklist for powder hoppers
● Troubleshooting common issues
● Sustainability and lifecycle considerations
● Final recommendations
● FQAS
In modern manufacturing, agriculture, and coating applications, automatic spray systems rely on reliable powder hoppers to deliver consistent material flow. Selecting the right hopper can improve application uniformity, reduce downtime, and extend equipment life. This article surveys top-rated powder hoppers suited for automatic spray systems, highlighting design features, material compatibility, performance expectations, and practical usage tips.
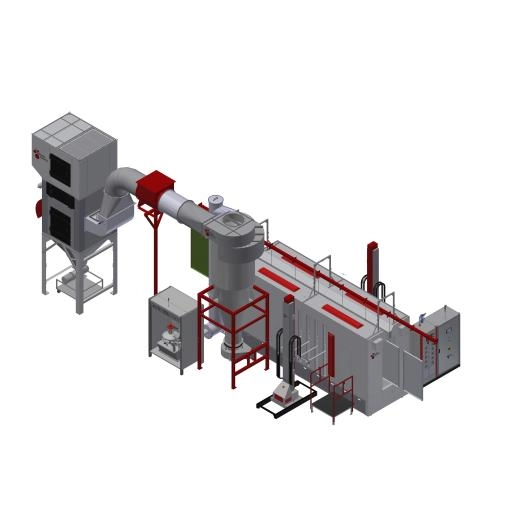
Understanding the role of powder hoppers
Powder hoppers serve as the storage and feeding reservoirs for dry powders used in spray processes. They regulate material flow, prevent bridging and rat-holing, and work in tandem with feeders and atomizers to ensure steady deposition. A well-chosen hopper minimizes clogging, provides easy maintenance, and supports precise process control. When evaluating hoppers, consider capacity, discharge rate, material compatibility, cleaning requirements, and compatibility with your spray system's feeder mechanism.
Key design features to look for
- Material construction: Common options include stainless steel for corrosion resistance and aluminum for lightweight duty. Some applications require coated surfaces to reduce adhesion or meet regulatory cleanability standards.
- Outlet configuration: The size, shape, and presence of quick-release clamps influence cleaning and replacement. Some models offer interchangeable orifice sizes to adjust flow.
- Venting and dust management: Integrated dust caps, vent filters, or explosion-proof designs help maintain a cleaner work environment and reduce operator exposure.
- Agitation and flow control: Internal agitators or baffles prevent compaction and bridging, ensuring consistent discharge.
- Compatibility with feeders: The hopper should align with the feeder mechanism, whether it's a screw feeder, vibratory feeder, or gravity-based system. Proper alignment reduces wear and improves throughput.
- Cleaning and sanitation: Hygienic finishes, smooth interior welds, and removable components facilitate cleaning, especially in food, pharma, or cosmetics contexts.
Capacity and discharge rate considerations
The optimal hopper capacity depends on production run length, cycle times, and downtime between cycles. A larger hopper can reduce changeover frequency but may add weight, cleaning complexity, and cost. Discharge rate should match the feeder's intake requirements and the spray system's deposition targets. When in doubt, select a hopper with adjustable or multiple discharge settings to accommodate process variability.
Material compatibility and coatings
Powders vary in bulk density, abrasiveness, and chemical reactivity. Ensure the hopper material resists wear from abrasive powders and does not react with components. Use coatings or surface finishes that minimize powder adherence and facilitate cleaning. For highly reactive or sensitive powders, consider inert liners or specialized coatings to preserve powder quality and prevent contamination.
Cleaning, sanitation, and regulatory considerations
Industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics mandate stringent cleanability. Pick hoppers with seamless interiors, removable components, and approved coatings. Establish a standardized cleaning protocol and designate dedicated tools to prevent cross-contamination. Document material compatibility and cleaning validation to satisfy audits or regulatory inspections.
Installation and integration tips
- Verify compatibility with your spray system's feeder and controller, including calibration procedures for flow accuracy.
- Ensure proper mounting height and access for maintenance tasks.
- Plan for drainage and waste handling to avoid powder buildup around the unit.
- Wire and electrical connections should comply with safety standards, especially in explosion-hazard environments.
Popular materials and brands
While many manufacturers offer powder hoppers, some brands stand out for reliability, ease of use, and durability. When evaluating options, review warranty terms, service networks, spare parts availability, and customer reviews. Prioritize suppliers with documented performance data and clear installation guidelines.
Maintenance best practices
- Schedule regular inspections of seals, gaskets, and discharge outlets.
- Inspect agitation mechanisms for wear and alignment.
- Clean interiors to prevent material buildup that could affect flow.
- Keep the exterior surfaces free from dust and corrosion to protect structural integrity.
Customization options worth considering
- Optional sanitary finishes for easy cleaning.
- Interchangeable outlet sizes to adapt to different feeders.
- Integrated dust collection or filtration attachments.
- Inert or corrosion-resistant liners for sensitive powders.
- Quick-release clamps or modular components to simplify maintenance.
Environmental and safety considerations
Powder handling can generate airborne particulates. Use appropriate ventilation, dust collection systems, and personal protective equipment. For hazardous powders, ensure confinement with sealed enclosures and proper lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance.
Selecting the right hopper for your application
- Assess powder characteristics: flowability, cohesiveness, and abrasiveness.
- Define production schedule: batch size, cycle time, and downtime.
- Identify system integration points: feeder type, control interfaces, and cleaning requirements.
- Consider future needs: scalability, maintenance access, and regulatory compliance.
Case study: optimizing a coating line
A coating line faced inconsistent coating thickness due to powder segregation and bridging in the hopper. After selecting a hopper with an anti-bridging design, variable discharge options, and a removable liner, the line achieved a more uniform spray pattern and reduced downtime for cleaning. The upgrade also simplified validation documentation for audits.
Practical tips for evaluating vendors
- Request performance data and real-world case studies similar to your application.
- Inquire about cleaning procedures, downtime, and ease of maintenance.
- Check for compatibility with existing spray system controllers and feeders.
- Ask about spare parts availability, lead times, and warranty coverage.
Maintenance checklist for powder hoppers
- Inspect for signs of wear, corrosion, or dents.
- Verify discharge outlets and seals are intact and functional.
- Confirm feeder alignment and calibration is up to date.
- Clean interior surfaces and remove any powder residue.
- Test venting and filtration components for proper operation.
Troubleshooting common issues
- Inconsistent discharge: Check for bridging, moisture buildup, or misalignment with the feeder.
- Powder leakage around seals: Inspect gaskets and seals; replace if worn.
- Excessive dust: Ensure proper sealing, venting, and filtration; verify enclosure integrity.
- Rapid wear of outlet components: Consider higher-grade materials or protective liners.
Sustainability and lifecycle considerations
Choosing durable, recyclable materials and designing for easy disassembly can extend the hopper's life and reduce environmental impact. When possible, select suppliers with take-back or recycling programs for worn components to minimize waste.
Final recommendations
- Prioritize hoppers with anti-bridging features and adjustable discharge settings to accommodate varying powders and process conditions.
- Ensure material compatibility and easy cleaning, especially in regulated industries.
- Verify system compatibility and maintenance support before purchase.
FQAS
1. How do I determine the right hopper capacity for my line?
Calculate your average production run length, cycle time, and downtime, then choose a capacity that minimizes changeovers without adding excessive weight or cleaning burden.
2. What coatings are best for reducing powder adhesion?
Smooth, hydrophobic coatings such as certain PTFE-based liners or specialized non-stick interior finishes reduce powder adhesion and simplify cleaning.
3. Can I retrofit an existing system with a new hopper?
Yes, if the feeder interface, mounting points, and discharge dimensions are compatible. Plan for calibration and potential control system updates.
4. What maintenance frequency is recommended for powder hoppers?
Cleaning frequency depends on powder type and regulatory requirements; at minimum, perform a thorough clean during scheduled maintenance and after any change in product or batch.
5. Which safety measures should accompany hopper installations?
Use proper ventilation and dust collection, ensure explosion-proof ratings for hazardous environments, and enforce PPE and lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance.
Hot Tags: China, Global, OEM, private label, manufacturers, factory, suppliers, manufacturing company










































 .
. 